Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Adrenal gland
- 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
- Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Endocrine Society, The Korean Adrenal Study Group of Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):597-618. Published online October 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1789

- 3,568 View
- 495 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Primary aldosteronism (PA) is a common, yet underdiagnosed cause of secondary hypertension. It is characterized by an overproduction of aldosterone, leading to hypertension and/or hypokalemia. Despite affecting between 5.9% and 34% of patients with hypertension, PA is frequently missed due to a lack of clinical awareness and systematic screening, which can result in significant cardiovascular complications. To address this, medical societies have developed clinical practice guidelines to improve the management of hypertension and PA. The Korean Endocrine Society, drawing on a wealth of research, has formulated new guidelines for PA. A task force has been established to prepare PA guidelines, which encompass epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care. The Korean clinical guidelines for PA aim to deliver an evidence-based protocol for PA diagnosis, treatment, and patient monitoring. These guidelines are anticipated to ease the burden of this potentially curable condition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation of Histopathologic Subtypes of Primary Aldosteronism with Clinical Phenotypes and Postsurgical Outcomes
Chang Ho Ahn, You-Bin Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hee Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Correlation of Histopathologic Subtypes of Primary Aldosteronism with Clinical Phenotypes and Postsurgical Outcomes

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
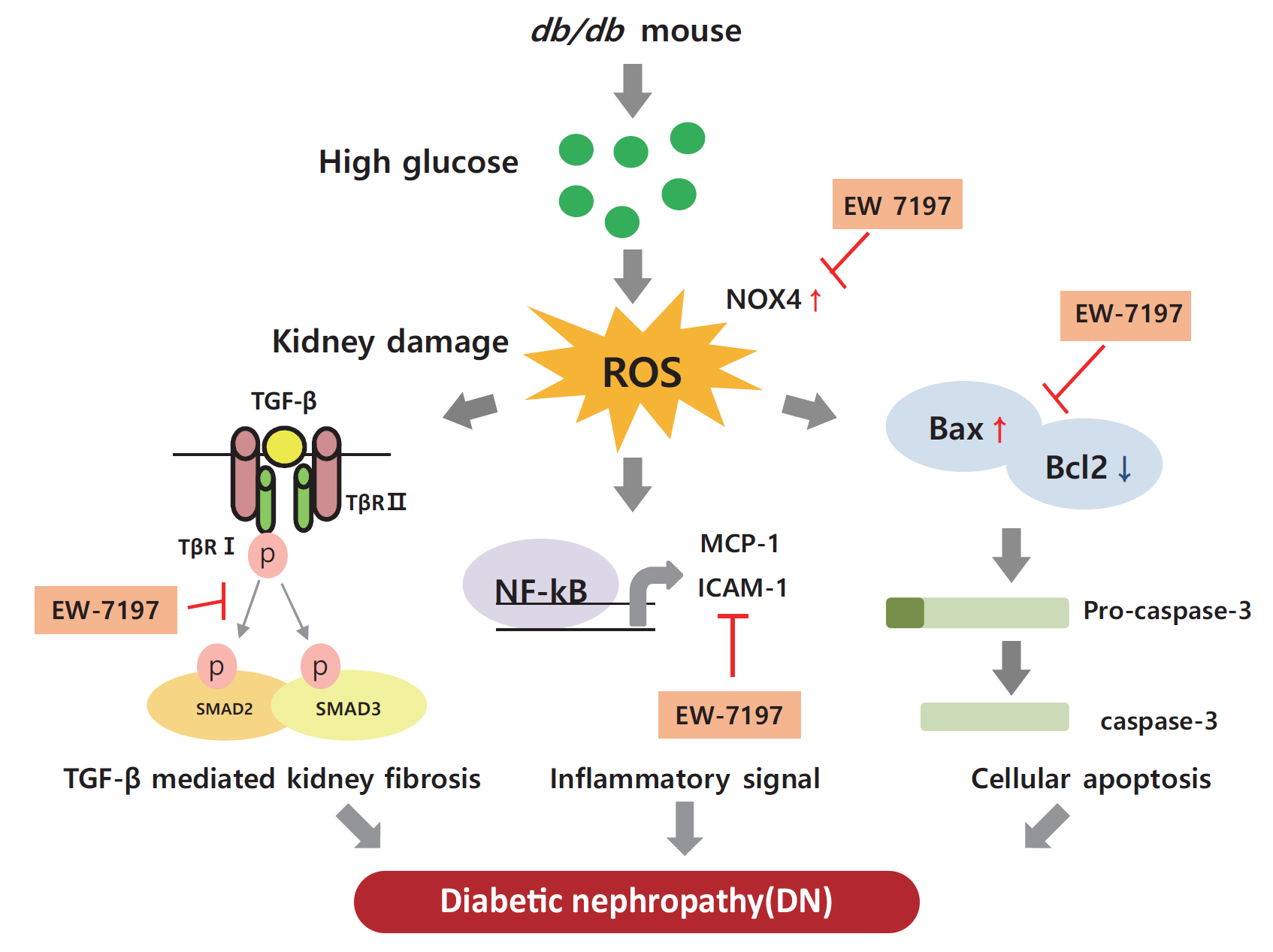
- EW-7197 Attenuates the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice through Suppression of Fibrogenesis and Inflammation
- Kyung Bong Ha, Weerapon Sangartit, Ah Reum Jeong, Eun Soo Lee, Hong Min Kim, Soyeon Shim, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Dae-Kee Kim, Eun Young Lee, Choon Hee Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):96-111. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1305
- 4,026 View
- 182 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is characterized by albuminuria and accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) in kidney. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) plays a central role in promoting ECM accumulation. We aimed to examine the effects of EW-7197, an inhibitor of TGF-β type 1 receptor kinase (ALK5), in retarding the progression of DN, both in vivo, using a diabetic mouse model (db/db mice), and in vitro, in podocytes and mesangial cells.
Methods
In vivo study: 8-week-old db/db mice were orally administered EW-7197 at a dose of 5 or 20 mg/kg/day for 10 weeks. Metabolic parameters and renal function were monitored. Glomerular histomorphology and renal protein expression were evaluated by histochemical staining and Western blot analyses, respectively. In vitro study: DN was induced by high glucose (30 mM) in podocytes and TGF-β (2 ng/mL) in mesangial cells. Cells were treated with EW-7197 (500 nM) for 24 hours and the mechanism associated with the attenuation of DN was investigated.
Results
Enhanced albuminuria and glomerular morphohistological changes were observed in db/db compared to that of the nondiabetic (db/m) mice. These alterations were associated with the activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway. Treatment with EW-7197 significantly inhibited TGF-β signaling, inflammation, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic mice and renal cells.
Conclusion
EW-7197 exhibits renoprotective effect in DN. EW-7197 alleviates renal fibrosis and inflammation in diabetes by inhibiting downstream TGF-β signaling, thereby retarding the progression of DN. Our study supports EW-7197 as a therapeutically beneficial compound to treat DN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics
Ziqin Deng, Tao Fan, Chu Xiao, He Tian, Yujia Zheng, Chunxiang Li, Jie He
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: role of polyphenols
Qi Jin, Tongtong Liu, Yuan Qiao, Donghai Liu, Liping Yang, Huimin Mao, Fang Ma, Yuyang Wang, Liang Peng, Yongli Zhan
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of a Curcumin Derivative and Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I Inhibitor Combination on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Na Won Park, Su Ho Jo, Soyeon Shim, Dae-Kee Kim, Chan Mug Ahn, Choon Hee Chung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 500. CrossRef
- TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics

- Adrenal Gland
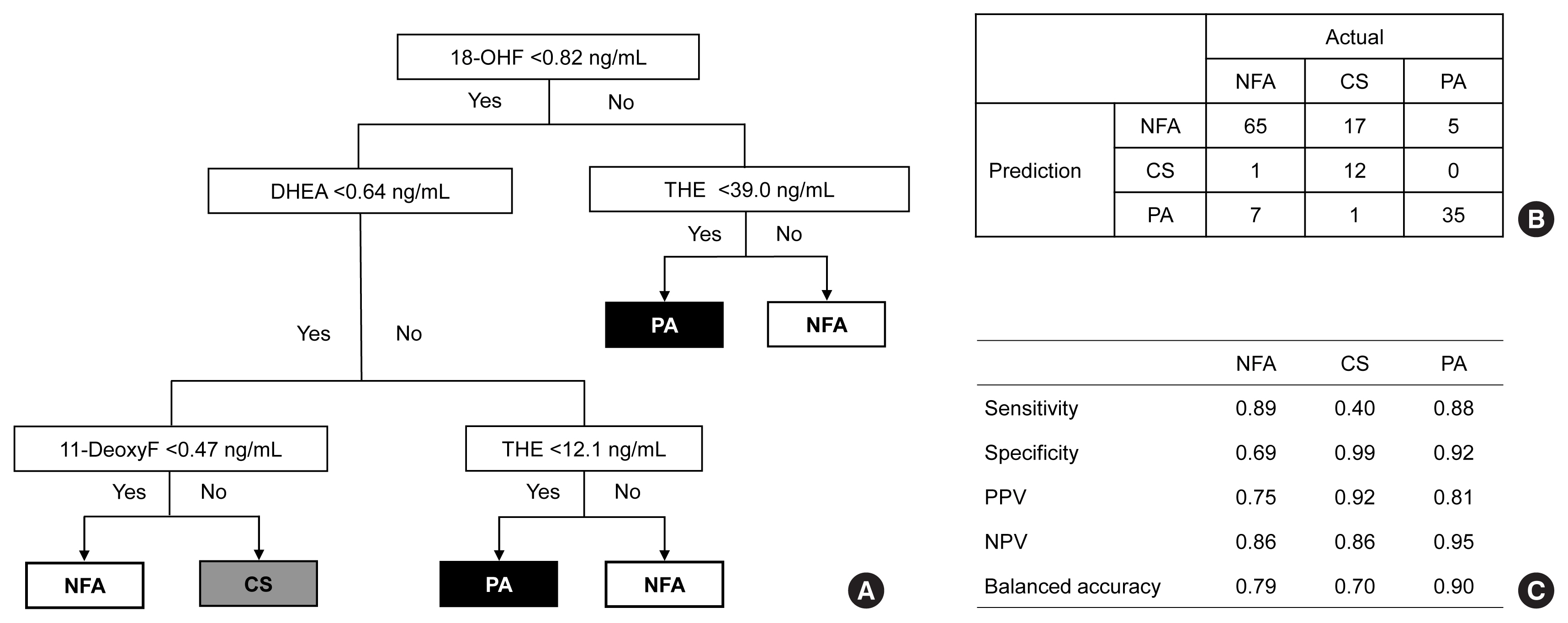
- Metabolic Subtyping of Adrenal Tumors: Prospective Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
- Eu Jeong Ku, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sihoon Lee, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Yumie Rhee, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Wan Chun, Soon-Jib Yoo, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Ho Chan Cho, A Ram Hong, Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1131-1141. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1149
- 5,184 View
- 211 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Conventional diagnostic approaches for adrenal tumors require multi-step processes, including imaging studies and dynamic hormone tests. Therefore, this study aimed to discriminate adrenal tumors from a single blood sample based on the combination of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and machine learning algorithms in serum profiling of adrenal steroids.
Methods
The LC-MS-based steroid profiling was applied to serum samples obtained from patients with nonfunctioning adenoma (NFA, n=73), Cushing’s syndrome (CS, n=30), and primary aldosteronism (PA, n=40) in a prospective multicenter study of adrenal disease. The decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), and extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) were performed to categorize the subtypes of adrenal tumors.
Results
The CS group showed higher serum levels of 11-deoxycortisol than the NFA group, and increased levels of tetrahydrocortisone (THE), 20α-dihydrocortisol, and 6β-hydroxycortisol were found in the PA group. However, the CS group showed lower levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate derivative (DHEA-S) than both the NFA and PA groups. Patients with PA expressed higher serum 18-hydroxycortisol and DHEA but lower THE than NFA patients. The balanced accuracies of DT, RF, and XGBoost for classifying each type were 78%, 96%, and 97%, respectively. In receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis for CS, XGBoost, and RF showed a significantly greater diagnostic power than the DT. However, in ROC analysis for PA, only RF exhibited better diagnostic performance than DT.
Conclusion
The combination of LC-MS-based steroid profiling with machine learning algorithms could be a promising one-step diagnostic approach for the classification of adrenal tumor subtypes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks
Nathan Mullen, James Curneen, Padraig T Donlon, Punit Prakash, Irina Bancos, Mark Gurnell, Michael C Dennedy
Endocrine Reviews.2024; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Steroid profiling in adrenal disease
Danni Mu, Dandan Sun, Xia Qian, Xiaoli Ma, Ling Qiu, Xinqi Cheng, Songlin Yu
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117749. CrossRef - Plasma steroid profiling combined with machine learning for the differential diagnosis in mild autonomous cortisol secretion from nonfunctioning adenoma in patients with adrenal incidentalomas
Danni Mu, Xia Qian, Yichen Ma, Xi Wang, Yumeng Gao, Xiaoli Ma, Shaowei Xie, Lian Hou, Qi Zhang, Fang Zhao, Liangyu Xia, Liling Lin, Ling Qiu, Jie Wu, Songlin Yu, Xinqi Cheng
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mild autonomous cortisol secretion: pathophysiology, comorbidities and management approaches
Alessandro Prete, Irina Bancos
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum and hair steroid profiles in patients with nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma undergoing surgery: A prospective observational study
Seung Shin Park, Yong Hwy Kim, Ho Kang, Chang Ho Ahn, Dong Jun Byun, Man Ho Choi, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2023; 230: 106276. CrossRef - Recent Updates on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Seung Shin Park, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 373. CrossRef - LC-MS based simultaneous profiling of adrenal hormones of steroids, catecholamines, and metanephrines
Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Seung Woon Myung, Man Ho Choi
Journal of Lipid Research.2023; 64(11): 100453. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Adrenal Tumors in an Unselected Screening Population
Ying Jing, Jinbo Hu, Rong Luo, Yun Mao, Zhixiao Luo, Mingjun Zhang, Jun Yang, Ying Song, Zhengping Feng, Zhihong Wang, Qingfeng Cheng, Linqiang Ma, Yi Yang, Li Zhong, Zhipeng Du, Yue Wang, Ting Luo, Wenwen He, Yue Sun, Fajin Lv, Qifu Li, Shumin Yang
Annals of Internal Medicine.2022; 175(10): 1383. CrossRef
- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
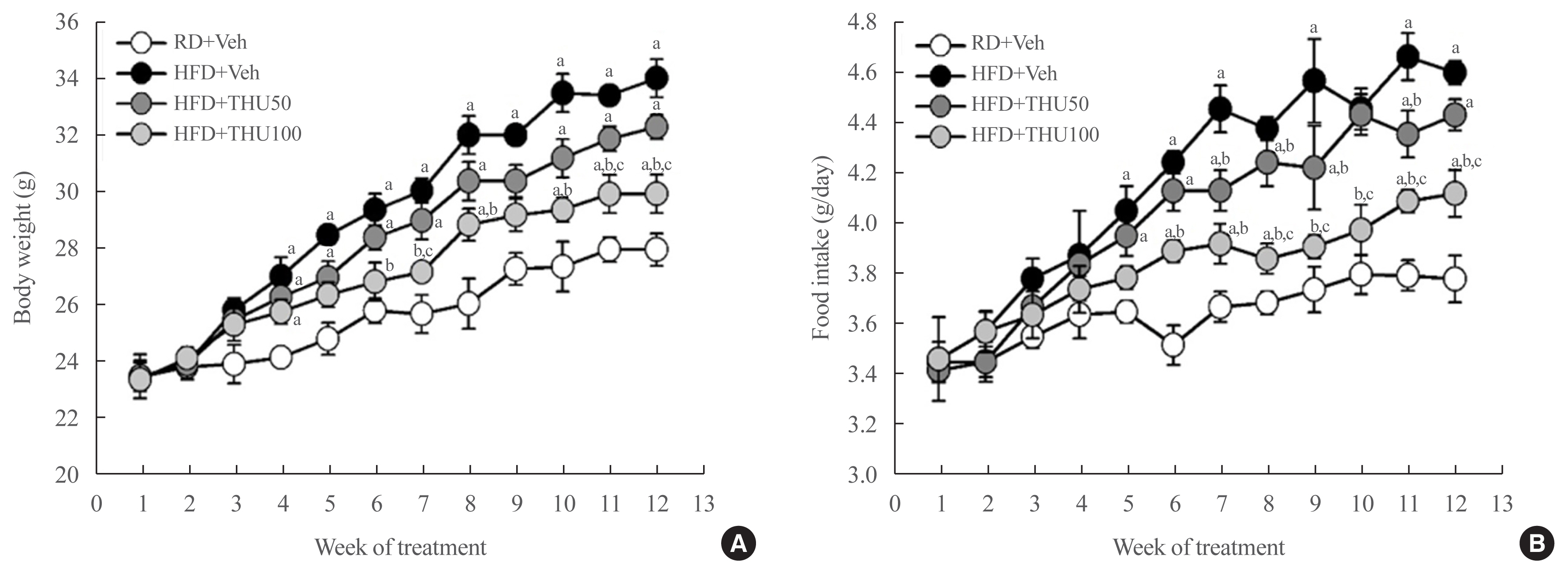
- Tetrahydrocurcumin Ameliorates Kidney Injury and High Systolic Blood Pressure in High-Fat Diet-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice
- Weerapon Sangartit, Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Hong Min Kim, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Eun Young Lee, Choon Hee Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):810-822. Published online August 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.988
- 4,100 View
- 165 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Activation of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is implicated in the pathogenesis of kidney injury and hypertension. We aimed to investigate the protective effect of tetrahydrocurcumin (THU) on intrarenal RAS expression, kidney injury, and systolic blood pressure (SBP) in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced type 2 diabetic mice.
Methods
Eight-week-old male mice were fed a regular diet (RD) or HFD for 12 weeks, and THU (50 or 100 mg/kg/day) was intragastrically administered with HFD. Physiological and metabolic changes were monitored and the expression of RAS components and markers of kidney injury were assessed.
Results
HFD-fed mice exhibited hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia compared to those in the RD group (P<0.05). Kidney injury in these mice was indicated by an increase in the ratio of albumin to creatinine, glomerular hypertrophy, and the effacement of podocyte foot processes. Expression of intrarenal angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin II type I receptor, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase-4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 was also markedly increased in HFD-fed mice. HFD-fed mice exhibited elevated SBP that was accompanied by an increase in the wall thickness and vascular cross-sectional area (P<0.05), 12 weeks post-HFD consumption. Treatment with THU (100 mg/kg/day) suppressed intrarenal RAS activation, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced SBP, thus, attenuating kidney injury in these mice.
Conclusion
THU alleviated kidney injury in mice with HFD-induced type 2 diabetes, possibly by blunting the activation of the intrarenal RAS/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase IV (NOX4)/monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) axis and by lowering the high SBP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Development of Dyslipidemia in Chronic Kidney Disease and Associated Cardiovascular Damage, and the Protective Effects of Curcuminoids
Zeltzin Alejandra Ceja-Galicia, Ana Karina Aranda-Rivera, Isabel Amador-Martínez, Omar Emiliano Aparicio-Trejo, Edilia Tapia, Joyce Trujillo, Victoria Ramírez, José Pedraza-Chaverri
Foods.2023; 12(5): 921. CrossRef - Translation Animal Models of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biochemical and Histological Phenotypes, Advantages and Limitations
Wenting Luo, Shiyun Tang, Xiang Xiao, Simin Luo, Zixuan Yang, Wei Huang, Songqi Tang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1297. CrossRef - Curcumin ameliorates focal segmental glomerulosclerosis by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress in podocytes
Hui Zhang, Qing-Qing Dong, Hua-Pan Shu, Yu-Chi Tu, Qian-Qian Liao, Li-Jun Yao
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2023; 746: 109728. CrossRef - An examination of the protective effects and molecular mechanisms of curcumin, a polyphenol curcuminoid in diabetic nephropathy
Xiaoyu Zhu, Xingli Xu, Chigang Du, Yanping Su, Lixue Yin, Xiaoqiu Tan, Hui Liu, Yiru Wang, Lei Xu, Xinghua Xu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 153: 113438. CrossRef - An integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental study identified key biomarkers CD300A or CXCL1, pathways and immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy mice
WEI LIANG, QIANG LUO, ZONGWEI ZHANG, KEJU YANG, ANKANG YANG, QINGJIA CHI, HUAN HU
BIOCELL.2022; 46(8): 1989. CrossRef
- The Development of Dyslipidemia in Chronic Kidney Disease and Associated Cardiovascular Damage, and the Protective Effects of Curcuminoids

- Two Cases of Graves Disease Associated The Empty Sella Syndrome.
- Yeun Jong Choi, Hong Seung Kim, Eui Ryun Park, Young Gu Shin, Choon Hee Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(4):517-522. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,403 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The empty sella syndrome is characterized by obesity, frequent pregnancy, headache and high blood pressure, but its exact cause remains unknown. Usually the incomplete diaphragmatic sella has been considered as the cause of the empty sella syndrome, but some authors recently have suggested that the antipituitary antibody way be related to development of pituitary atrophy and the pituitary empty sella syndrome, and thus it may be clinically useful as screening test for the empty sella syndrome. We experienced two empty sella syndromes associated Graves disease and applied the antipituitary antibody as the diagnostic tool of the empty sella syndrome. But none of this two patients had antipituitary antibody and we report these cases with reviews of literatures.

- A Case of Calcitonin Secreting Pheochromocytoma.
- Joo Won Byun, Young Goo Shin, Choon Hee Chung, Young Jun Won, Yoon Jong Choi, Eui Ryun Park, Mi Duck Lee, Chang Ho Song, Mi Youn Cho, Sung Jun Kang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(3):343-347. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,487 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine producing turnor and raise with less than 0.1% of hypertensive patients. It is developed, most commonly, in sporadic pheochromocytoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. Therefore, when hypercalcitoninemia is found in a patient with pheochromocytoma, the possibility of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 or the ectopic secretion of calcitonin must be considered. Recently we experienced a 45 year old male patient with sporadic pheochrornocytoma. He also had hypercalcitoninemia and normocalcemia. After the removal of pheochromocytoma, serum calcitnnin level returned to normal. Secretion of calcitonin was confirmed by immunohisto- chemical stain.

- A Case of Autoimmune Hypoglycemia Due to Insulin Receptor Antibody Associated with Empty Sella Syndrome.
- Hong Seung Kim, Young Jun Won, Hyung Jun Lee, Yoon Jong Choi, Do Sik Yoon, Young Goo Shin, Choon Hee Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):119-123. Published online November 7, 2019
- 976 View
- 21 Download

- A Case of Turner Syndrome Associated with Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Empty Sella.
- Hong Seung Kim, Joo Won Byun, Do Sik Yoon, Byung Gi Seo, Young Goo Shin, Choon Hee Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):114-118. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,072 View
- 16 Download

- Tuberculosis of the Thyroid Gland.
- Chang Ho Song, Choon Hee Chung, Young Joon Weon, Mi Deok Lee, Seong Jin Park, Won Sik Lee, Mee Yon Cho, Young Kyung Kim, Seung Min Kim, Seong Joon Kang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):428-433. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,013 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tuberculosis the thyroid gland occurs only rarely and a few records are available in Korea, despite of high prevalence of tuberculosis. The authors experienced a case of young woman with tuberculosis of the thyroid gland and meninges. Tuberculosis of the thyroid gland was confirmed by demonstration of acid-fast bacilli and granuloma with caseation necrosis on surgical specimen. Description of case profile and a brief review of literature are made.

- A Case of Thyrotoxic Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis Presenting as Cardiac Arrest.
- Chang Ho Song, Choon Hee Chung, Young Joon Weon, Mi Deok Lee, Seong Jin Park, Young Goo Shin, Won Sik Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):424-427. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,051 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Periodic paralysis associated with thyrotoxicosis is characterized by intermittent flaccid paralysis of the skeletal muscle. The paralysis usually involve the skeletal muscle of the limbs, especially lower extrimities. In general, sensory function is intact. Involvement of respiratory, ocular or bulbar muscles is very rare, but bulbar and respiratoy invelvement may prove fatal. It is very rare a case that has severe clinical manifestation such as cardiac arrest. We report a case of thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis presenting as cardiac arrest.

- Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Hyperthyroidism.
- Ju Yong Lee, Chang Ho Song, Byeung Su Yu, Choon Hee Chung, Yoon Sok Chung, Hyeon Man Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(1):52-57. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,224 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyperthyroidism is a well known cause of atrial fibrillation. It is also known that control of hyperthyroidism can usually curb thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation and restore sinus rhythm. In this study, 282 patients with hyperthyroidism were investigated to quantify the incidence of atrial fibrillation, and to identify the vulnerable groups. In addition, we compared two groups of subjects with atrial fibrillation-one group with hyperthyroidism and the other group without - to study their reversion rate to sinus rhythm. Lastly, we investigated the factors affecting reversion to sinus rhythm in patients with thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation.The results were follows;1) Among 282 patients with hyperthyroidism, 35 cases(12.4%) had atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillations were more prevalent among male patient(19.4%) and elderly patients(42.9%) than female patients(10.0%) and young patients(10.0%).2) Reversion to normal sinus rhythm in patients with thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation(39.3%) was significantly higher than that in patients without hyperthyroidism(17.4%, p<0.001).3) Reversion to normal sinus rhythm was achieved within 28 weeks from the beginnig of antithyroid treatment in patients with thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation. Although there were no significant differences in mean age, sex ratio, and initial and follow-up thyroid hormone levels between the reversion group and non-reversion group, associated heart diseases were more prevalent in the latter group(18.2% vs. 47.1%).It can be concluded that thyrotoxic atrial fibrillations were more common in male patient and elderly patient groups, and could be frequently reverted to normal sinus rhythm by antithyroid treatment. We also suggest that the duration of artrial fibrillation(from intial onset of the condition), and associated heart diseases, may be important predictive factors for the reversion of atrial fibrillation in patients with hyperthyroidism.

- A Case of Thyrotoxic Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis Presenting as Cardiac Arrest.
- Chang Ho Song, Choon Hee Chung, Young Goo Shin, Young Joon Weon, Mi Deok Lee, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):175-178. Published online November 6, 2019
- 927 View
- 17 Download

- Seasonal Variation in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in The Elderly in Korean.
- Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Yoon Sok Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(2):121-127. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,066 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The seasonal variations in the parameters of calcium metabolism including 25-hydroxyvitamin D were analyzed in 19 free-living elderly subjects (mean age:68.7±6.7 yr) in Seoul. Mean serum total calcium concentration was 9.0±0.3 mg/dl in March and had risen to 9.3±0.3mg/dl in the following September(p<0.001). Despite their comparable calcium intake. Serum phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase concentrations did not show any seasonal variations, whereas serum PTH concentrations were significantly lower in September than in March(20.1±8.6 vs. 32.5±8.4 pg/ml, p<0.001). Seasonal changes in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations were also found between the value(17.3±6.9 ng/ml) in March and that (28.5±7.4 ng/ml) in September(p<0.001). There was a significant correlation between seasonal increase in 25-hydroxyvitamin D and seasonal reduction in serum PTH/Cr(r=-0.5394, p<0.05). This study suggests that the winter minimum of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and the elevated PTH may be a contributing risk factor for the development of osteopenia especially in the elderly individuals. When exposure to sunlight is reduced, as in the case of nursing home population, an additional exogenous form of the vitamin D may be advisable.

- Endocrine Research
- Effects of Oxytocin on Cell Proliferation in a Corticotroph Adenoma Cell Line
- Jung Soo Lim, Young Woo Eom, Eun Soo Lee, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Ja-Young Kwon, Junjeong Choi, Choon Hee Chung, Young Suk Jo, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):302-313. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.302
- 5,054 View
- 74 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Oxytocin (OXT) has been reported to act as a growth regulator in various tumor cells. However, there is a paucity of data on the influence of OXT on cell proliferation of corticotroph adenomas. This study aimed to examine whether OXT affects cell growth in pituitary tumor cell lines (AtT20 and GH3 cells) with a focus on corticotroph adenoma cells.
Methods Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were conducted with AtT20 cells to confirm the effects of OXT on hormonal activity; flow cytometry was used to assess changes in the cell cycle after OXT treatment. Moreover, the impact of OXT on proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), nuclear factor κB, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway was analyzed by Western blot.
Results OXT treatment of 50 nM changed the gene expression of OXT receptor and pro-opiomelanocortin within a short time. In addition, OXT significantly reduced adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion within 1 hour. S and G2/M populations of AtT20 cells treated with OXT for 24 hours were significantly decreased compared to the control. Furthermore, OXT treatment decreased the protein levels of PCNA and phosphorylated extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (P-ERK) in AtT20 cells.
Conclusion Although the cytotoxic effect of OXT in AtT20 cells was not definite, OXT may blunt cell proliferation of corticotroph adenomas by altering the cell cycle or reducing PCNA and P-ERK levels. Further research is required to investigate the role of OXT as a potential therapeutic target in corticotroph adenomas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased proliferation and neuronal fate in prairie vole brain progenitor cells cultured in vitro: effects by social exposure and sexual dimorphism
Daniela Ávila-González, Italo Romero-Morales, Lizette Caro, Alejandro Martínez-Juárez, Larry J. Young, Francisco Camacho-Barrios, Omar Martínez-Alarcón, Analía E. Castro, Raúl G. Paredes, Néstor F. Díaz, Wendy Portillo
Biology of Sex Differences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anterior pituitary gland synthesises dopamine from l‐3,4‐dihydroxyphenylalanine (l‐dopa)
Santiago Jordi Orrillo, Nataly de Dios, Antonela Sofía Asad, Fernanda De Fino, Mercedes Imsen, Ana Clara Romero, Sandra Zárate, Jimena Ferraris, Daniel Pisera
Journal of Neuroendocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Increased proliferation and neuronal fate in prairie vole brain progenitor cells cultured in vitro: effects by social exposure and sexual dimorphism

- Miscellaneous
- An Unusual Case of Meningioma Showing Increased CaSR Expression with Parathyroid Carcinoma
- Jin Sae Yoo, Hong Min Kim, Sera Kim, Tak Ho Kang, Mee Yon Cho, Choon Hee Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):133-134. Published online January 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.133
- 3,141 View
- 43 Download


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



